
Introduction: Choosing the Right LiDAR Tool: A Critical Decision for Modern Surveyors
“With the construction industry needing to build 13,000 buildings every day until 2050 to support over 7 billion people projected to live in cities”, surveyors are under immense pressure to deliver faster, more accurate site data than ever before.
Yet, common challenges persist:
- Difficult terrain and inaccessible areas
- Time lost on manual or repetitive site visits
- Rework due to incomplete or inaccurate measurements
- Tight timelines and budget constraints
This is where 3D laser scan to BIM, powered by LiDAR, has become indispensable. Whether airborne or ground-mounted, LiDAR enables precise reality capture, minimizing time on-site and maximizing data reliability.
But not all LiDAR tools are created equal. Choosing between a LiDAR drone and a tripod-based terrestrial scanner can significantly impact:
- The accuracy of your final model
- The efficiency of your workflow
- And the cost-effectiveness of your project
This checklist will help you make that choice with confidence, based on your site conditions, project scope, and performance needs.
Overview of LiDAR technology - Precision from Light
LiDAR - Light Detection and Ranging is a remote sensing technology that uses laser pulses to accurately measure distances between the scanner and surrounding surfaces. These pulses, often emitted at thousands of times per second, generate dense point clouds that form highly accurate 3D representations of physical environments.
For surveyors dealing with complex, large-scale, or hard-to-access sites, LiDAR solves critical pain points by offering:
- Millimeter-level accuracy for detailed documentation
- Fast, large-area data capture with minimal disruption
- Reduced time on-site and fewer repeat visits
- Direct compatibility with CAD and BIM platforms
LiDAR enables surveyors to capture reality with speed, safety, and confidence.
What Are LiDAR Drones?
LiDAR drones are unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) equipped with LiDAR sensors that capture high-resolution 3D data from the air. They emit rapid laser pulses toward the ground and measure the time it takes for each pulse to return, creating accurate geospatial point clouds.
For surveyors facing challenges like large, inaccessible, or hazardous sites, LiDAR drones offer:
- Rapid topographic mapping over vast areas
- Minimal ground access needed, ideal for dense vegetation or steep terrain
- Reduced field time and crew requirements
- High accuracy with lower safety risks
They're widely used in civil engineering, forestry, mining, and infrastructure planning, where speed and scale matter most.
What Are Tripod-Based Terrestrial Laser Scanners?
Tripod-based laser scanners, also known as terrestrial LiDAR scanners, are stationary devices mounted on tripods that rotate 360° to emit laser beams and capture precise distance measurements of surrounding surfaces. The result is a high-density point cloud with exceptional spatial accuracy.
For surveyors working in tight, detail-heavy, or GPS-denied environments, these scanners solve key challenges by offering:
- Millimeter-level detail for architectural and heritage documentation
- Reliable interior scanning of buildings, tunnels, and industrial plants
- Ideal performance in urban areas with obstructions or limited airspace
- Consistent accuracy in controlled, static conditions
They are the go-to solution for detailed and precision-driven 3D Laser Scan to BIM Services in USA.
LiDAR Drones vs. Terrestrial Laser Scanners - Pros and Cons
Both LiDAR drones and terrestrial laser scanners offer powerful advantages, but their effectiveness depends on the context of use. Below is a breakdown of their key pros and cons to help surveyors make an informed, project-specific decision.
LiDAR Drones: Pros and Cons
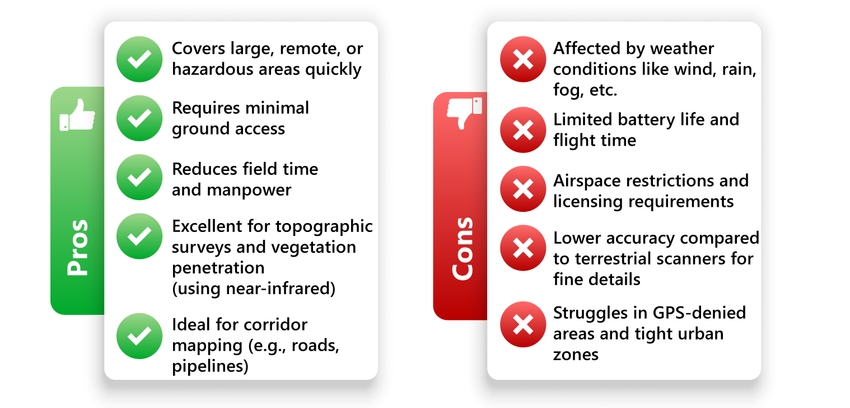
Terrestrial Laser Scanners: Pros and Cons
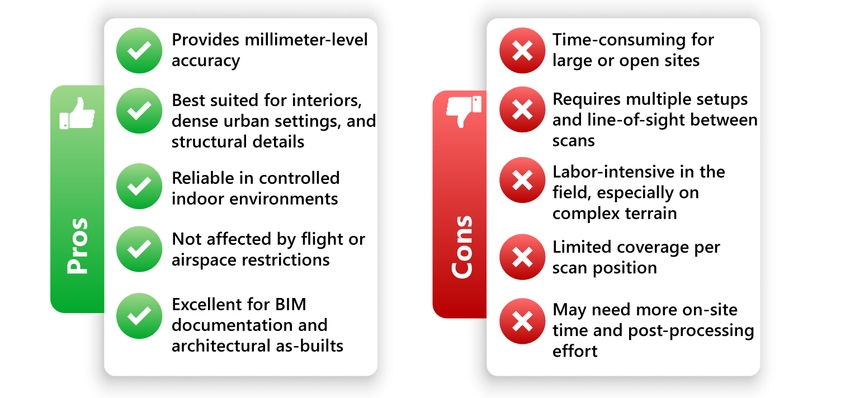
These pros and cons help clarify when and where each technology performs best, ensuring that surveyors select the most effective tool based on project conditions.
Key Comparison: LiDAR Drones vs. Terrestrial Tripod Scanners
Selecting the right LiDAR system is critical for maximizing accuracy, efficiency, and field safety. This comparison highlights how LiDAR drones and tripod-based scanners perform across key parameters that matter most to surveyors.
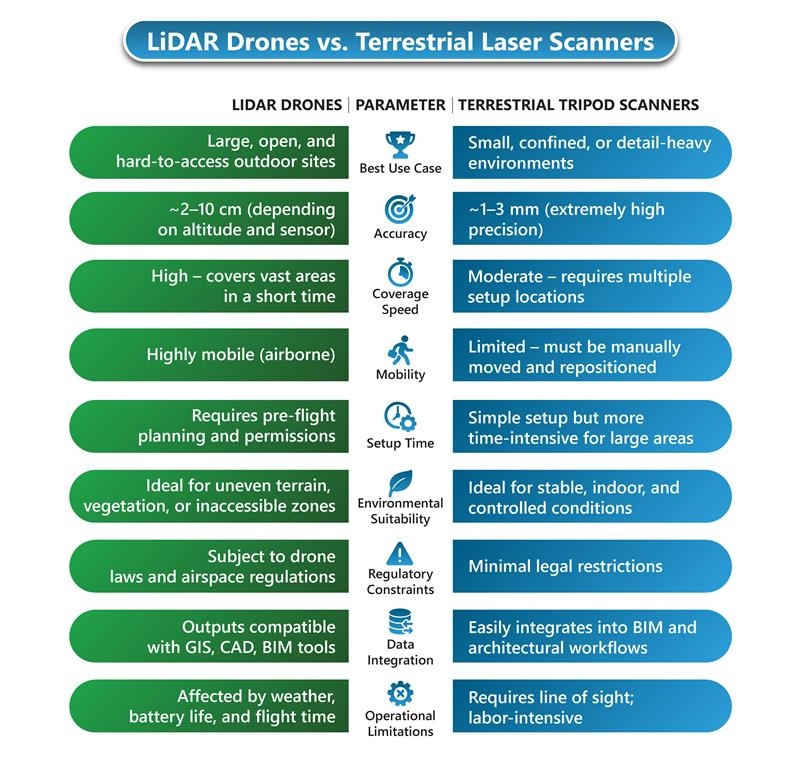
Best Use Cases for Each Technology: LiDAR Drones vs. Tripod Scanners
Choosing between a LiDAR drone and a terrestrial tripod scanner isn’t just about specs—it’s about matching the tool to the environment.
Below is a situational breakdown to help surveyors pick the right technology for common project types:
Urban Buildings
Tripod Terrestrial Scanner Preferred
- Narrow spaces, reflective surfaces, and GPS denial make drones difficult to operate.
- Tripod scanners offer millimeter-level accuracy for façades, interiors, and architectural features.
Forested Areas
LiDAR Drone Preferred
- An aerial view avoids dense underbrush and difficult terrain.
- Can penetrate vegetation using near-infrared pulses to capture bare-earth surfaces effectively.
Infrastructure Corridors (Roads, Railways, Pipelines)
LiDAR Drone Preferred
- Covers long linear distances quickly and safely with fewer setups.
- Great for reducing time on active or hazardous sites.
Heritage Sites
Tripod Terrestrial Scanner Preferred
- Captures fine architectural details, textures, and intricate geometry with high precision.
- Essential when preservation-grade accuracy is required.
Construction Sites
Depends on the Site Phase and Scope
- LiDAR Drones are effective for topographic surveys, progress tracking, and large-scale earthworks.
- Tripod Terrestrial Scanners are better for structural verification, MEP layouts, and clash detection indoors.
Using the right technology for the right context helps surveyors avoid costly rework, speed up data collection, and improve deliverable accuracy across project types.
Future Trends in LiDAR: Smarter, Faster 3D Laser Scan to BIM Workflows
The future of 3D laser scan to BIM is evolving rapidly, addressing key pain points like long processing times, data gaps, and high equipment costs. Emerging trends are making reality capture more accessible and intelligent:
- Hybrid Workflows: Combining drone and terrestrial LiDAR for complete site coverage, outdoors and indoors, without sacrificing accuracy.
- AI-Powered Processing: Machine learning accelerates point cloud classification, noise filtering, and BIM-ready model generation.
- Affordable, Advanced Sensors: New-generation LiDAR hardware is becoming lighter, cheaper, and more accurate, enabling wider adoption across small and mid-sized firms.
These innovations empower surveyors to deliver faster, more detailed, and cost-effective BIM outputs.
Final Thoughts: Choosing the Right Tool for Surveyors
When it's about 3D laser scanning, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution. LiDAR vs Laser Scanning excel in speed and area coverage, while tripod-based terrestrials provide unmatched detail and precision in confined spaces. Rather than choosing one over the other, many surveyors now adopt hybrid workflows, using both technologies to capture complete, accurate datasets across varied environments.
This complementary approach solves key pain points like access limitations, data blind spots, and costly rework, ensuring seamless BIM integration and better project outcomes.
Need help turning raw scans into intelligent BIM models?








